Page 23 - HUDCO-SHELTER-APR21
P. 23
THEME PAPER
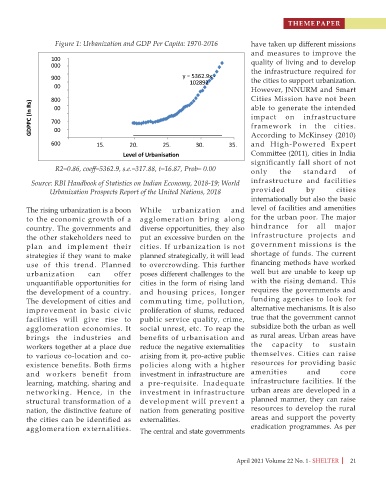
Figure 1: Urbanization and GDP Per Capita: 1970-2016 have taken up different missions
and measures to improve the
quality of living and to develop
the infrastructure required for
y = 5362.9x -
102892 the cities to support urbanization.
However, JNNURM and Smart
Cities Mission have not been
Rs)
(In
able to generate the intended
GDPPC framework in the cities.
impact on infrastructure
According to McKinsey (2010)
15. 20. 25. 30. 35. and High-Powered Expert
Level of Urbanisa on Commi ee (2011), cities in India
significantly fall short of not
R2=0.86, coeff=5362.9, s.e.=317.88, t=16.87, Prob= 0.00 only the standard of
Source: RBI Handbook of Statistics on Indian Economy, 2018-19; World infrastructure and facilities
Urbanization Prospects Report of the United Nations, 2018 provided by cities
internationally but also the basic
The rising urbanization is a boon While urbanization and level of facilities and amenities
to the economic growth of a agglomeration bring along for the urban poor. The major
country. The governments and diverse opportunities, they also hindrance for all major
the other stakeholders need to put an excessive burden on the infrastructure projects and
plan and implement their cities. If urbanization is not government missions is the
strategies if they want to make planned strategically, it will lead shortage of funds. The current
use of this trend. Planned to overcrowding. This further financing methods have worked
urbanization can offer poses different challenges to the well but are unable to keep up
unquantifiable opportunities for cities in the form of rising land with the rising demand. This
the development of a country. and housing prices, longer requires the governments and
The development of cities and commuting time, pollution, funding agencies to look for
improvement in basic civic proliferation of slums, reduced alternative mechanisms. It is also
facilities will give rise to public service quality, crime, true that the government cannot
agglomeration economies. It social unrest, etc. To reap the subsidize both the urban as well
brings the industries and benefits of urbanisation and as rural areas. Urban areas have
workers together at a place due reduce the negative externalities the capacity to sustain
to various co-location and co- arising from it, pro-active public themselves. Cities can raise
existence benefits. Both firms policies along with a higher resources for providing basic
and workers benefit from investment in infrastructure are amenities and core
learning, matching, sharing and a pre-requisite. Inadequate infrastructure facilities. If the
networking. Hence, in the investment in infrastructure urban areas are developed in a
structural transformation of a development will prevent a planned manner, they can raise
nation, the distinctive feature of nation from generating positive resources to develop the rural
the cities can be identified as externalities. areas and support the poverty
agglomeration externalities. The central and state governments eradication programmes. As per
April 2021 Volume 22 No. 1- SHELTER 21