Page 15 - HUDCO-SHELTER-OCT21
P. 15
THEME PAPER
MITIGATION AND result, more heat is trapped in India with its diverse agro-
ADAPTATION earth’s atmosphere instead of climatic and morphological
radiating out into space. This zones is particularly affected
Without the so-called makes clear that there is a close
greenhouse gases, including relationship among carbon by GHG/carbon emissions.
carbon dioxide, methane, emissions, climate change According to the Indian
nitrous oxide, and water and disaster vulnerability. Network for Climate Change
vapour, earth would be Assessment in 2010, 58 per
too cold to inhabit. These Climate change mitigation cent of the total emissions
gases in earth’s atmosphere generally involves reduction were caused by the energy
absorb and emit heat energy, in emissions of greenhouse sector, followed by the
creating the greenhouse gases (GHGs). Mitigation may industrial sector at 22 per cent,
effect that keeps our planet’s also be achieved by increasing and remaining at 20 per cent
temperature liveable. Water the capacity of carbon sinks,
vapour is the most plentiful e.g., through reforestation by solid and liquid waste and
greenhouse gas on the planet, (IPCC 2007). Adaptation forestry. Of the total carbon
accounting for about 60 per to global warming seeks to dioxide (CO ) emissions, 85%
2
cent of the current greenhouse reduce the vulnerability of are contributed by the energy
effect. Even ozone helps trap biological systems to climate sector, while 78% of nitrous
some of the heat that makes change effects (UNFCCC, oxide (NO )emissions were
2
life on Earth possible. Since 2010). Adaptive capacity due to the agriculture sector.
the industrial revolution, is closely linked to social
people have burned vast and economic development According to the United
amounts of coal, petroleum, (IPCC, 2007). The mitigation Nations Framework on the
and other fossil fuels to and adaptation strategy for Convention on Climate
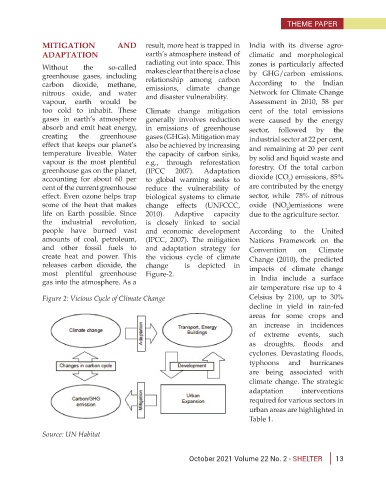
create heat and power. This the vicious cycle of climate Change (2010), the predicted
releases carbon dioxide, the change is depicted in impacts of climate change
most plentiful greenhouse Figure-2.
gas into the atmosphere. As a in India include a surface
air temperature rise up to 4°
Figure 2: Vicious Cycle of Climate Change Celsius by 2100, up to 30%
decline in yield in rain-fed
areas for some crops and
an increase in incidences
of extreme events, such
as droughts, floods and
cyclones. Devastating floods,
typhoons and hurricanes
are being associated with
climate change. The strategic
adaptation interventions
required for various sectors in
urban areas are highlighted in
Table 1.
Source: UN Habitat
October 2021 Volume 22 No. 2 - SHELTER 13