Page 67 - Shelter-October-2022
P. 67
POLICY REVIEW
taken by the beneficiaries, were under BLC, 2.39 million (2022) also highlight the
and (5) Affordable Rental (19.6%) under CLSS, 2.06 underachievement of
Housing Complexes (ARHC) million (16.8%) under AHP, ISSR owing to the various
scheme launched in July and 0.43 million (3.5%) under legislative and administrative
2020 to address the rental ISSR (MoHUA, 2022). conflicts arising during
housing needs of urban project implementation.
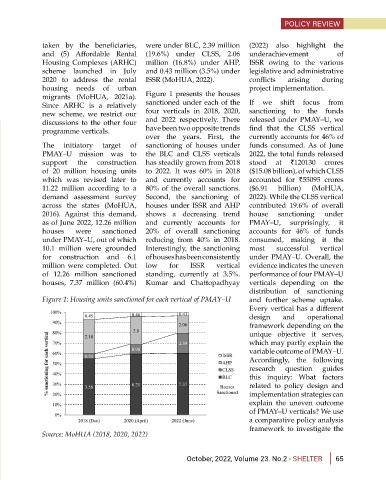
migrants (MoHUA, 2021a). Figure 1 presents the houses
Since ARHC is a relatively sanctioned under each of the If we shift focus from
new scheme, we restrict our four verticals in 2018, 2020, sanctioning to the funds
discussions to the other four and 2022 respectively. There released under PMAY–U, we
programme verticals. have been two opposite trends find that the CLSS vertical
over the years. First, the currently accounts for 46% of
The initiatory target of sanctioning of houses under funds consumed. As of June
PMAY–U mission was to the BLC and CLSS verticals 2022, the total funds released
support the construction has steadily grown from 2018 stood at `120130 crores
of 20 million housing units to 2022. It was 60% in 2018 ($15.08 billion), of which CLSS
which was revised later to and currently accounts for accounted for `55095 crores
11.22 million according to a 80% of the overall sanctions. ($6.91 billion) (MoHUA,
demand assessment survey Second, the sanctioning of 2022). While the CLSS vertical
across the states (MoHUA, houses under ISSR and AHP contributed 19.6% of overall
2016). Against this demand, shows a decreasing trend house sanctioning under
as of June 2022, 12.26 million and currently accounts for PMAY–U, surprisingly, it
houses were sanctioned 20% of overall sanctioning accounts for 46% of funds
under PMAY–U, out of which reducing from 40% in 2018. consumed, making it the
10.1 million were grounded Interestingly, the sanctioning most successful vertical
for construction and 6.1 of houses has been consistently under PMAY–U. Overall, the
million were completed. Out low for ISSR vertical evidence indicates the uneven
of 12.26 million sanctioned standing, currently at 3.5%. performance of four PMAY–U
houses, 7.37 million (60.4%) Kumar and Chattopadhyay verticals depending on the
distribution of sanctioning
Figure 1: Housing units sanctioned for each vertical of PMAY–U and further scheme uptake.
Every vertical has a different
design and operational
framework depending on the
unique objective it serves,
which may partly explain the
variable outcome of PMAY–U.
Accordingly, the following
research question guides
this inquiry: What factors
related to policy design and
implementation strategies can
explain the uneven outcome
of PMAY–U verticals? We use
a comparative policy analysis
framework to investigate the
Source: MoHUA (2018, 2020, 2022)
October, 2022, Volume 23. No.2 - SHELTER 65