Page 68 - Shelter-October-2022
P. 68
POLICY REVIEW
reasons behind the variations domains (Lodge, 2007). This proposed by Schneider and
between the verticals. comparative lens allows the Ingram (1997) to compare
researchers to understand the four PMAY–U programme
Comparative analysis of variations between different verticals. The policy
PMAY–U verticals policies addressing the same design framework offers
Comparative analysis problem (housing in this researchers an approach to
in public policy entails paper) and draw lessons for comparing and analysing
using comparative logic to further policy development. the fundamental elements
systematically investigate the We apply the comparative of policies, including goals,
similarities and differences analysis approach to the agents, target populations, and
across different policy policy design framework tools that are common features
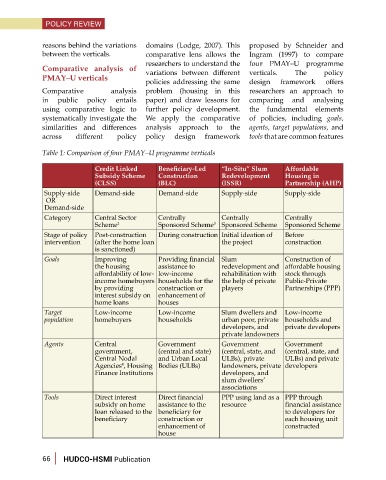
Table 1: Comparison of four PMAY–U programme verticals
Credit Linked Beneficiary-Led “In-Situ” Slum Affordable
Subsidy Scheme Construction Redevelopment Housing in
(CLSS) (BLC) (ISSR) Partnership (AHP)
Supply-side Demand-side Demand-side Supply-side Supply-side
OR
Demand-side
Category Central Sector Centrally Centrally Centrally
Scheme 2 Sponsored Scheme 3 Sponsored Scheme Sponsored Scheme
Stage of policy Post-construction During construction Initial ideation of Before
intervention (after the home loan the project construction
is sanctioned)
Goals Improving Providing financial Slum Construction of
the housing assistance to redevelopment and affordable housing
affordability of low- low-income rehabilitation with stock through
income homebuyers households for the the help of private Public-Private
by providing construction or players Partnerships (PPP)
interest subsidy on enhancement of
home loans houses
Target Low-income Low-income Slum dwellers and Low-income
population homebuyers households urban poor, private households and
developers, and private developers
private landowners
Agents Central Government Government Government
government, (central and state) (central, state, and (central, state, and
Central Nodal and Urban Local ULBs), private ULBs) and private
Agencies , Housing Bodies (ULBs) landowners, private developers
4
Finance Institutions developers, and
slum dwellers’
associations
Tools Direct interest Direct financial PPP using land as a PPP through
subsidy on home assistance to the resource financial assistance
loan released to the beneficiary for to developers for
beneficiary construction or each housing unit
enhancement of constructed
house
66 HUDCO-HSMI Publication