Page 80 - Shelter-October-2022
P. 80
CASE STUDIES
residents claimed that before infrastructure amenities that scheme. The parameters were
the redevelopment, the in turn have raised the level predicated on the notion of
unclean and substandard of living overall, produced different attributes and other
living environments a safe neighbourhood, and criteria needed for grading.
contributed to the spread of promoted social cohesiveness. The overall analysis was
disease, increasing their health based on the primary survey
care expenses, demoralising QUALITY OF LIFE observations. The study
or preventing them from A qualitative technique measured the quality of life
working, and compromising was used to determine in the in-situ resettlement
the community’s well-being. the effectiveness of community based on five
The implementation of the specific scheme features crucial parameters (F5):
programme, on the other in determining the quality household satisfaction;
hand, was intended to offer of life of beneficiaries after stakeholder satisfaction;
better social and physical the implementation of the housing operating costs;
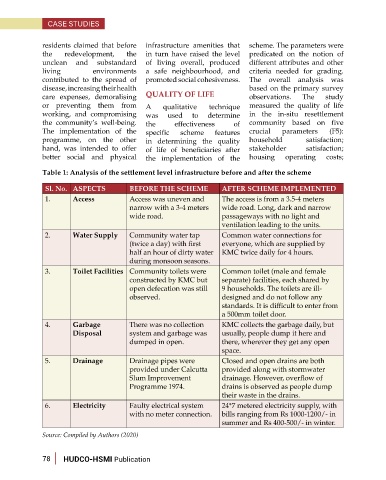
Table 1: Analysis of the settlement level infrastructure before and after the scheme
Sl. No. ASPECTS BEFORE THE SCHEME AFTER SCHEME IMPLEMENTED
1. Access Access was uneven and The access is from a 3.5-4 meters
narrow with a 3-4 meters wide road. Long, dark and narrow
wide road. passageways with no light and
ventilation leading to the units.
2. Water Supply Community water tap Common water connections for
(twice a day) with first everyone, which are supplied by
half an hour of dirty water KMC twice daily for 4 hours.
during monsoon seasons.
3. Toilet Facilities Community toilets were Common toilet (male and female
constructed by KMC but separate) facilities, each shared by
open defecation was still 9 households. The toilets are ill-
observed. designed and do not follow any
standards. It is difficult to enter from
a 500mm toilet door.
4. Garbage There was no collection KMC collects the garbage daily, but
Disposal system and garbage was usually, people dump it here and
dumped in open. there, wherever they get any open
space.
5. Drainage Drainage pipes were Closed and open drains are both
provided under Calcutta provided along with stormwater
Slum Improvement drainage. However, overflow of
Programme 1974. drains is observed as people dump
their waste in the drains.
6. Electricity Faulty electrical system 24*7 metered electricity supply, with
with no meter connection. bills ranging from Rs 1000-1200/- in
summer and Rs 400-500/- in winter.
Source: Compiled by Authors (2020)
78 HUDCO-HSMI Publication